Ovarian Cysts: Types, Symptoms, & Causes - All You Should Know

Women of all ages may be affected by ovarian cysts, which are fluid-filled sacs that form on the ovaries. While many women may experience them at some point in their lives, understanding the various types, symptoms, and causes of ovarian cysts is crucial for managing reproductive health. This comprehensive guide aims to provide insights into ovarian cysts, their implications for fertility, and when to seek medical attention. At our IVF centre in Jaipur, Rajasthan, we emphasize the importance of awareness and timely intervention for optimal reproductive health.
What Are Ovarian Cysts?
Ovarian cysts are a common occurrence during a woman’s menstrual cycle. Most of these cysts are benign (non-cancerous) and may not cause any symptoms. However, some can lead to complications that necessitate medical intervention. Ovarian cysts form when the follicles, which are fluid-filled sacs that hold eggs, do not release an egg as they should or do not dissolve after the egg has been released.
Types of Ovarian Cysts
Understanding the types of ovarian cysts can help women recognize their symptoms and seek appropriate treatment when necessary. The two most common types of ovarian cysts are functional cysts and pathological cysts.
1. Functional Cysts
The most prevalent kind of cysts are functional Cysts, which usually develop during the menstrual cycle. Two primary categories of functioning cysts exist:
• Follicular Cysts: These cysts occur when a follicle fails to release an egg during ovulation. The follicle develops into a cyst as it grows. Within a few menstrual cycles, the majority of follicular cysts go away on their own.
• Corpus Luteum Cysts: After the egg is released from the follicle, the remaining follicle transforms into the corpus luteum, which produces hormones. If the corpus luteum fills with fluid and doesn’t dissolve, it becomes a corpus luteum cyst. These cysts can also resolve on their own, but they may cause symptoms if they become large.
2. Pathological Cysts
Pathological cysts are less common and may require medical evaluation. They can be classified into two categories:
• Dermoid Cysts: These cysts develop from germ cells, which are responsible for producing eggs. Teeth, skin, and hair are among the tissues that can be found in dermoid cysts. They usually require surgical removal.
• Endometriomas: Women with endometriosis may develop endometriomas, which are cysts formed from endometrial tissue that grows on the ovaries. These cysts can cause pain and may interfere with fertility.
• Cystadenomas: These are cysts that develop from the cells on the outer surface of the ovary. They can be filled with a watery or mucous substance and may grow large. Surgical removal is often necessary.
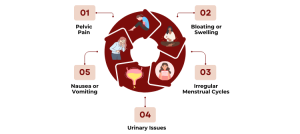
Symptoms of Ovarian Cysts
Many ovarian cysts do not cause noticeable symptoms, but when they do, women may experience:
• Pelvic Pain: This can range from mild discomfort to severe pain, often occurring during menstruation or sexual intercourse.
• Bloating or Swelling: A woman may feel a sense of fullness or pressure in the abdomen.
• Irregular Menstrual Cycles: Changes in the menstrual cycle, including missed periods or heavier-than-normal bleeding, can occur.
• Urinary Issues: Pressure from a large cyst can cause frequent urination or difficulty emptying the bladder completely.
• Changes in Bowel Habits: Some women may experience discomfort or changes in bowel habits, such as constipation.
• Nausea or Vomiting: Large cysts can lead to gastrointestinal symptoms due to pressure on the digestive system.
If a cyst ruptures, it can cause severe pain and internal bleeding, which may require immediate medical attention.
Causes of Ovarian Cysts
While the exact cause of ovarian cysts varies, several factors contribute to their development:
• Hormonal Imbalances: Fluctuations in hormones can lead to the formation of functional cysts during the menstrual cycle.
• Menstrual Cycle: Most cysts occur during the reproductive years, especially during the menstrual cycle.
• Endometriosis: Women with endometriosis are more likely to develop ovarian cysts due to the presence of endometrial tissue outside the uterus.
• Previous Ovarian Cysts: Women with a history of ovarian cysts are at a higher risk of developing new ones.
• Age: Hormonal changes during perimenopause can lead to an increased likelihood of cyst formation.
• Certain Medical Conditions: Conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) can lead to multiple cysts developing on the ovaries.
Diagnosis of Ovarian Cysts
If a woman experiences symptoms associated with ovarian cysts, her healthcare provider will typically conduct a thorough evaluation. This process may include:
1. Medical History Review: The provider will discuss symptoms, menstrual cycle history, and any relevant medical conditions.
2. Pelvic Exam: A pelvic examination allows the healthcare provider to check for any abnormalities, including cysts.
3. Imaging Tests: Ultrasound is commonly used to visualize the ovaries and assess the size and appearance of any cysts. In some cases, CT scans or MRI may be necessary.
4. Blood Tests: In certain situations, blood tests may be performed to measure hormone levels or rule out other conditions.
Treatment Options for Ovarian Cysts
Most ovarian cysts resolve on their own and do not require treatment. However, in cases where cysts cause significant symptoms or complications, treatment options may include:
1. Watchful Waiting
If a cyst is small and asymptomatic, a healthcare provider may recommend monitoring it over a few menstrual cycles. Regular follow-up ultrasounds can help track changes in size and appearance.
2. Medications
Birth control pills and other hormonal contraceptives can help control the menstrual cycle and stop new cysts from forming.
3. Surgery
Surgical intervention may be necessary for larger cysts, cysts that cause severe symptoms, or cysts suspected to be cancerous. The type of surgery performed may vary based on the cyst’s characteristics:
• Laparoscopy: This minimally invasive procedure allows for the removal of the cyst through small incisions. It typically involves quicker recovery and less pain.
• Laparotomy: In cases where a cyst is large or potentially cancerous, a larger incision may be required for removal.
Impact of Ovarian Cysts on Fertility
While most ovarian cysts are benign and do not impact fertility, certain types can pose challenges for women trying to conceive:
• Endometriomas: These cysts can disrupt normal ovarian function and may require treatment to enhance fertility.
• Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): Women with PCOS often develop multiple cysts and may face challenges with ovulation. Treating PCOS can improve fertility outcomes.
• Surgical Removal: In some cases, the surgical removal of cysts may impact ovarian reserve, especially if a significant amount of healthy tissue is removed.
Women experiencing infertility issues should consult a healthcare provider for a thorough evaluation. An experienced fertility specialist can recommend appropriate treatment options and monitor ovarian health.
Related- Understanding Unexplained Infertility: A Comprehensive Guide
Lifestyle Changes to Manage Ovarian Cysts
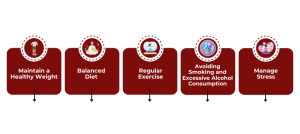
While not all ovarian cysts are preventable, certain lifestyle modifications may reduce the risk of developing them:
1. Maintain a Healthy Weight: Being overweight can disrupt hormonal balance and increase the risk of cyst formation, especially in women with PCOS.
2. Balanced Diet: Eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can support overall health and hormonal balance.
3. Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity helps maintain a healthy weight and supports hormonal regulation.
4. Avoiding Smoking and Excessive Alcohol Consumption: These habits can negatively impact reproductive health and increase the risk of cyst formation.
5. Manage Stress: Stress can affect hormonal balance, so practicing stress-reducing techniques like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing can be beneficial.
Conclusion
Ovarian cysts are common and often harmless, but understanding their types, symptoms, and causes is essential for women’s reproductive health. Recognizing when to seek medical attention can lead to timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment. At Nishant Fertility Care, we specialize in female infertility treatment in Jaipur and offer comprehensive care tailored to individual needs. If you have concerns about ovarian cysts or fertility, don’t hesitate to reach out for a consultation. Your health and well-being are our priority.
